Lead halide perovskites
Lead halide perovskites form the basis of a promising new technology in the field of photovoltaics. The efficiency of thin-film solar cells made purely from these materials has rocketed to > 22% within only a few years of research. Moreover, they are attractive as tandem layers in silicon solar cells. Despite this rapid progress, a number of questions regarding the basic properties of lead halide perovskites remain open.
Lead halide perovskites are complex ionic crystalline materials, since they contain both heavy elements and typically also organic components. They are mechanically soft, and atomic rearrangements can efficiently be induced by thermal or optical excitation. The resulting structural fluctuations modify the local electronic structure and affect the charge transport. Significant spin polarizations have been predicted to emerge.
We track the dynamics in the system using a combination of photoemission techniques, optical spectroscopy, and transport measurements. We put our focus on the (dynamical) electronic structure and especially on the possibility to generate an electronic spin polarization in lead halide perovskites by optical excitation. The goal of this research is to help develop a full description of the microscopic mechanisms in solar cells and spintronics devices made from perovskites and related materials. The experiments are carried out in close collaboration with our partners at the University of Erlangen-Nürnberg. The project is associated with the SPP 2196: Perovskite Semiconductors.
Contact
Project Funding
DFG project: Lead halide perovskites (associated with SPP 2196: “Perovskite Semiconductors”)
Publications
- , , , , , , , , , :
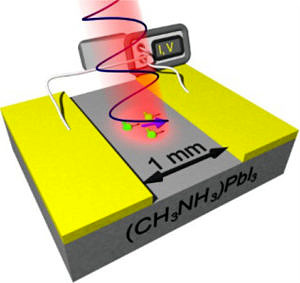
Structural fluctuations cause spin-split states in tetragonal (CH₃NH₃)PbI₃ as evidenced by the circular photogalvanic effect
In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 115 (2018), p. 9509-9514
ISSN: 0027-8424
DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1805422115
URL: https://www.pnas.org/doi/epdf/10.1073/pnas.1805422115 - , , , , , :
Assessing Temperature Dependence of Drift Mobility in Methylammonium Lead Iodide Perovskite Single Crystals
In: Journal of Physical Chemistry C 122 (2018), p. 5935-5939
ISSN: 1932-7447
DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b00341 - , , , , , , , , :
Temperature-dependent optical spectra of single-crystal (CH3NH3)PbBr3 cleaved in ultrahigh vacuum
In: Physical Review B - Condensed Matter and Materials Physics 95 (2017), Article No.: 075207
ISSN: 1550-235X
DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevB.95.075207 - , , , , , , , :
Giant Rashba Splitting in CH3NH3PbBr3 Organic-Inorganic Perovskite
In: Physical Review Letters 117 (2016), Article No.: 126401
ISSN: 0031-9007
DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.117.126401
URL: http://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevLett.117.126401